Generic Name:
alprazolam
Trade Name:
Xanax ® [Pfizer]
IUPAC Name:
8-chloro-6-cyclohexyl-1-methyl-
4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-
a][1,4]benzodiazepine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Tablet/orally disintegrating;
Extended release tablet/oral;
Concentrate/oral
Major Metabolites:
4-hydroxyalprazolam; a-hydroxyalprazolam
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
10/16/1981
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[XR Tablet]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H13ClN4
Molecular Mass:
308.765 g/mol
Indications:
Anxiety disorder; Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD); panic disorder
Possible Mechanism of Action:
Alprazolam is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (12).
Chemical Class:
triazolo analog of the 1,4 benzodiazepine class
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
amitriptyline hydrochloride
Common Chemical Name:
3-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo
[a,d] cycloheptene-5-
ylidene)-N,N-dimethyl-1-
propanamine hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
nortriptyline;
10-hydroxyamitriptyline;
10-hydroxynortriptyline
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
04/07/1961
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C20H24ClN
Molecular Mass:
313.864 g/mol
Major Depressive Disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Amitriptyline inhibits the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine (1). Amitriptyline acts as an antagonist at all subtypes of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (2). The drug also has antagonist activity at histamine H1 and H2 receptors, serotonin 5-HT2A receptors, and norepinephrine alpha-1 receptors (1). It also binds to histamine H4 receptors (11).
tertiary tricyclic (dibenzocycloheptadine derivative)
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
amitriptyline hydrochloride and
chlordiazepoxide
Trade Name:
Limbitrol ® [Valeant]
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
Initial Approval:
12/23/1977
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C36H37ClN4O
Molecular Mass:
613.619 g/mol
Moderate to severe depression associated with moderate to severe anxiety
Please refer to the entries for amitriptyline hydrochloride and chlordiazepoxide.

Generic Name:
amitriptyline hydrochloride and
perphenazine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
Initial Approval:
08/23/1965
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C41H50Cl2N4OS
Molecular Mass:
717.833 g/mol
Treatment of patients with moderate to severe anxiety and/or agitation and depressed mood; patients with depression in whom anxiety and/or agitation are moderate or severe; patients with anxiety and depression associated with chronic physical disease; patients in whom depression and anxiety cannot be clearly differentiated; schizophrenic patients who have associated symptoms of depression
Please refer to the entries for amitriptyline hydrochloride and perphenazine.

Generic Name:
amoxapine
Common Chemical Name:
2-chloro-11-(1-piperazinyldibenz-
[b,f][1,4]oxapine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
8-hydroxyamoxapine;
7-hydroxyamoxapine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
09/22/1980
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H16ClN3O
Molecular Mass:
313.781 g/mol
Depression in patients with neurotic or reactive depressive disorders as well as endogenous and psychotic depressions; depression accompanied by anxiety or agitation
Amoxapine inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine (5). The drug also inhibits glycine reuptake mediated by glycine transporter 2a (GLYT2a) (6). Amoxapine is an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A (7) and 5-HT2C receptors (7, 8). In addition, amoxapine is an antagonist at dopamine D2 receptors (9). It may also be an antagonist at alpha-1-adrenoceptors (130), histamine H1 receptors (130), and dopamine D4 receptors (9, 10). Finally, amoxapine binds with moderate affinity to alpha-2-adrenoceptors and binds with very low affinity to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (131).
tricyclic dibenzoxazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
aripiprazole
Trade Name:
Abilify ® [Bristol-Myers Squibb/Otsuka]
IUPAC Name:
7-[4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)
piperazin-1-yl]butoxy]-3,4-
dihydro-1H-quinolin-2-one
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Solution/oral;
Tablet/orally disintegrating;
Injectable/intramuscular
Major Metabolites:
dehydro-aripiprazole
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
11/15/2002
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C23H27Cl2N3O2
Molecular Mass:
448.385 g/mol
Schizophrenia; acute manic and mixed episodes associated with bipolar disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Depending on the cell type and function examined, aripiprazole is an agonist, partial agonist, or antagonist at dopamine D2 receptors (13). The drug is a partial agonist at dopamine D3 receptors (13). In addition, it is a partial agonist at serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors and an inverse agonist at serotonin 5-HT2B receptors (13). Aripiprazole also exhibits significant affinity for serotonin 5-HT7 receptors, alpha-1A-adrenoceptors, and histamine H1 receptors (13).
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
atomoxetine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Strattera ® [Eli Lilly]
IUPAC Name:
N-methyl-3-(2-methylphenoxy)-
3-phenyl-propan-1-amine
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolites:
4-hydroxyatomoxetine;
N-desmethylatomoxetine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
11/26/2002
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H22ClNO
Molecular Mass:
291.815 g/mol
ADHD
Atomoxetine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) (3). A major metabolite of atomoxetine, 4-hydroxyatomoxetine, is a partial agonist at kappa opioid receptors (4).
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
bupropion hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Wellbutrin ®, Zyban® [GlaxoSmithKline]
IUPAC Name:
1-(3-chlorophenyl)-2-tert-
butylamino-propan-1-one
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Extended release tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
hydroxybupropion; threohydrobupropion; erythrohydrobupropion
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/30/1985
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[SR]
[XL]
[Zyban]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C13H19Cl2NO
Molecular Mass:
276.202 g/mol
Major depressive disorder; smoking cessation aid
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Bupropion inhibits the norepinephrine and dopamine transporters with low potency (14). A metabolite of bupropion, hydroxybupropion, contributes to the drug's effects as a norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitor (14). The (2S,3S)- isomer of hydroxybupropion is a much more potent norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor than bupropion. Other bupropion metabolites may also contribute to the drug's effects at the norepinephrine and dopamine transporters (14). Bupropion is a noncompetitive antagonist at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors including the alpha3beta2, alpha4beta2, alpha3beta4, and alpha4beta4 subtypes (14, 15). Bupropion metabolites such as (2S,3S)-hydroxybupropion are also antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (14).
aminoketone
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
buspirone hydrochloride
Trade Name:
BuSpar ® [Bristol-Myers Squibb]
IUPAC Name:
8-[4-(4-pyrimidin-2-
ylpiperazin-1-yl)butyl]-8-
azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-
dione
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
1-pyrimidinylpiperazine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
09/29/1986
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C21H32ClN5O2
Molecular Mass:
421.964 g/mol
Anxiety disorders or short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety
Buspirone is a partial agonist at serotonin 5-HT1A receptors (17). It also acts as an antagonist at dopamine D2 receptors, but its affinity for these receptors is 16-fold weaker than its affinity for 5-HT1A receptors (18).
Chemical Class:
piperazinyl derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Librium ® [Valeant]
Common Chemical Name:
9-chloro-5-hydroxy-N-methyl-
6-
phenyl-2,5-
diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-
1,6,8,10-tetraen-3-imine
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolites:
desmethylchlordiazepoxide;
demoxepam;
desmethyldiazepam;
oxazepam
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
02/24/1960
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C16H15Cl2N3O
Molecular Mass:
336.215 g/mol
Anxiety disorders or short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety; withdrawal symptoms of acute alcoholism; preoperative apprehension and anxiety
Chlordiazepoxide is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (19, 20).
Chemical Class:
2-keto benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
chlorpromazine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Thorazine ® [GlaxoSmithKline]
IUPAC Name:
3-(2-chlorophenothiazin-10-
yl)-
N,N-dimethyl-propan-1-
amine hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Injectable/injection;
Syrup/oral;
Concentrate/oral
Major Metabolites:
7-hydroxychlorpromazine;
3-hydroxychlorpromazine;
chlorpromazine N-oxide; chlorpromazine sulfoxide; norchlorpromazine; norchlorpromazine sulfoxide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
11/20/1957
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[Injectable]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H19ClN2S
Molecular Mass:
318.865 g/mol
Schizophrenia; nausea and vomiting; relief of restlessness and apprehension before suregery; acute intermittent porphyria; adjunct in the treatment of tetanus; manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder; relief of intractable hiccups; for the treatment of severe behavioral problems in children (1 to 12 years of age) marked by combativeness and/or explosive hyperexcitable behavior (out of proportion to immediate provocations), and in the short-term treatment of hyperactive children who show excessive motor activity with accompanying conduct disorders consisting of some or all of the following symptoms: impulsivity, difficulty sustaining attention, aggressivity, mood lability and poor frustration tolerance
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Chlorpromazine is an antagonist at dopamine D1 and D2 receptors (21) as well as D3 (22) and D4 receptors (23). The drug may be an inverse agonist at dopamine D2S receptors (133). It also exhibits antagonist activity at serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors (24). In addition, chlorpromazine is an antagonist at alpha-1A-adrenoceptors (25), alpha-1B-adrenoceptors (25), alpha-2B-adrenoceptors (26), alpha-2C-adrenoceptors (26), and histamine H1 receptors (27). The drug also binds with moderately high affinity to muscarinic M1, M3, M4, and M5 receptors (28). Finally, chlorpromazine binds with high affinity to serotonin 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 receptors (29).
Chemical Class:
aliphatic phenothiazine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
citalopram hydrobromide
Trade Name:
Celexa ® [Forest Labs]
IUPAC Name:
1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-1-
(4-fluorophenyl)-3H-
isobenzofuran-5-carbonitrile
hydrobromide
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Tablet/orally disintegrating;
Solution/oral
Major Metabolites:
demethylcitalopram; didemethylcitalopram;
citalopram-N-oxide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
07/17/1998
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C20H22BrFN2O
Molecular Mass:
405.304 g/mol
Indications:
Major depressive disorder
Citalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) (16).
Chemical Class:
racemic bicyclic phthalane derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
clomipramine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Anafranil ® [Tyco Healthcare]
Common Chemical Name:
3-chloro-5-[3-
(dimethylamino)propyl]-10,11-
dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine
monohydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolites:
desmethylclomipramine;
8-hydroxyclomipramine;
8-hydroxydesmethylclomipramine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/29/1989
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C19H24Cl2N2
Molecular Mass:
351.313 g/mol
Indications:
OCD in adults, children, and adolescents
Clomipramine inhibits the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine (30). The drug also binds to serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT3 receptors, dopamine D2 and D3 receptors, and alpha-1-adrenoceptors (30). Clomipramine acts as an antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (31), but the muscarinic receptor subtypes that it affects have not been identified. The drug is also an antagonist at histamine H1 receptors (32). Finally, clomipramine binds to serotonin 5-HT6 receptors (116).
Chemical Class:
dibenzazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
clonazepam
Trade Name:
Klonopin ® [Roche]
IUPAC Name:
6-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-nitro-
2,5-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-
5,8,10,12-tetraen-3-one
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Tablet/orally disintegrating
Major Metabolite:
7-aminoclonazepam
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
06/04/1975
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula: C15H10ClN3O3
Molecular Mass:
315.711 g/mol
Indications:
Panic disorder; alone or as an adjunct in the treatment of the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (petit mal variant), akinetic seizures, and myoclonic seizures; in patients with absence seizures (petit mal) who have failed to respond to succinimides, clonazepam may be useful
Possible Mechanism of Action:
Clonazepam is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (12).
Chemical Class:
3-hydroxy benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
clorazepate dipotassium
Trade Name:
Tranxene ® [Ovation]
IUPAC Name:
dipotassium 9-chloro-3-oxo-6-
phenyl-2,5-
diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-
5,8,10,12-tetraene-4-carboxylic
acid hydroxide
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolites:
nordiazepam;
oxazepam
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
06/23/1972
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C16H12ClK2N2O4+
Molecular Mass:
409.927 g/mol
Anxiety disorders or short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety; adjunctive therapy in the management of partial seizures; withdrawal symptoms of acute alcoholism
Clorazepate is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (33).
Chemical Class:
2-keto benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
clozapine
Trade Name:
Clozaril ® [Novartis]
Common Chemical Name:
8-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-
piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo [b,e]
[1,4] diazepine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Tablet/orally disintegrating
Major Metabolite:
N-desmethylclozapine;
clozapine N-oxide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
09/26/1989
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Clozaril tablet]
[Orally disintegrating tablet]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C18H19ClN4
Molecular Mass:
326.823 g/mol
Treatment-resistant schizophrenia; reduction in the risk of recurrent suicidal behavior in schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorders
Possible Mechanisms of Action: Clozapine is a low affinity inverse agonist at dopamine D2S receptors (106, 133) and a high affinity antagonist at D4 receptors (34). It is also an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A (35), 5-HT2B (36), and 5-HT6 receptors (37). Clozapine is an inverse agonist at serotonin 5-HT2C (38) and 5-HT7 receptors (39). The drug is an antagonist at alpha-1A-adrenoceptors and alpha-1B-adrenoceptors (25). Clozapine is also an antagonist at alpha-2A-adrenoceptors and alpha-2C-adrenoceptors (40). Clozapine binds with relatively high affinity to alpha-2B-adrenoceptors (41); it likely acts as an antagonist at these receptors. Depending on cell type and receptor density, clozapine is an antagonist or partial agonist at muscarinic M1, M2, M3, and M4 receptors (42, 43). The drug is also an antagonist at muscarinic M5 receptors (44). Finally, clozapine is an antagonist at histamine H1 receptors (27).
Chemical Class:
tricyclic dibenzodiazepine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
desipramine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Norpramin ® [Sanofi-Aventis]
Common Chemical Name:
5 H -Dibenz[ bf ]azepine-5-
propanamine, 10,11-dihydro-
N-methyl-,
monohydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
2-hydroxydesipramine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
11/20/1964
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C18H23ClN2
Molecular Mass:
302.841 g/mol
Various depressive syndromes, especially endogenous depression
Desipramine is a high affinity norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (45). It exhibits relatively low affinity for histamine H1 receptors, muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, and alpha-1-adrenoceptors (45).
Chemical Class:
secondary tricyclic dibenzazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
desvenlafaxine succinate
Trade Name:
Pristiq ® [Wyeth]
IUPAC Name:
butanedioic acid; 4-[2-dimethylamino-1-(1-
hydroxycyclohexyl)ethyl]phenol; hydrate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Extended release tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
desvenlafaxine glucoronide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
02/29/2008
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C20H33NO7
Molecular Mass:
399.47852 g/mol
Major depressive disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Desvenlafaxine inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine (154). It has a greater affinity for the serotonin transporter (154).
Chemical Class:
the succinate salt of the isolated major active metabolite of venlafaxine, a phenethylamine bicyclic derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:
Generic Name:
dexmethylphenidate hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Focalin ® [Novartis]
Common Chemical Name:
alpha-phenyl-2-piperidineacetate
hydrochloride, (R,R’)-(+)-
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Extended release capsule/oral
Major Metabolite:
d-ritalinic acid
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
11/13/2001
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Focalin Tablet]
[Focalin XR Capsule]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C14H19NO2•HCl
Molecular Mass:
269.77 g/mol
ADHD
Dexmethylphenidate inhibits the dopamine transporter and, to a lesser degree, the norepinephrine transporter (46). The drug offers a better therapeutic index than racemic threo-methylphenidate hydrochloride (Ritalin®) (47).
Chemical Class:
d-threo enantiomer of racemic methylphenidate hydrocholoride
2D Structure:

Generic Name:
dextroamphetamine sulfate
Trade Name:
Dexedrine ® [GlaxoSmithKline]
IUPAC Name:
1-phenylpropan-2-amine;
sulfuric
acid
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Extended release capsule/oral;
Solution/oral
Major Metabolites:
p-hydroxyamphetamine;
p-hydroxynorephedrine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
02/26/1976
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C18H28N2O4S
Molecular Mass:
368.492 g/mol
ADHD; narcolepsy
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
At plasmalemmal catecholamine transporters, amphetamine indirectly increases the efflux of cytosolic catecholamines
so that they are released into the synaptic cleft (144). The drug causes the release of norepinephrine more potently than it causes the release of dopamine; it is much less effective as a serotonin releasing agent (144) The drug also directly inhibits norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake at higher concentrations (144). Amphetamine- induced activation of protein kinase C (PKC) beta(II) is likely to be responsible for the drug's effect on dopamine efflux (145). Na+ is cotransported with amphetamine as it enters neurons via catecholamine transporters; amphetamine-induced increases in intracellular Na+ may stimulate Na+/Ca2+ antiporters, resulting in an influx of Ca2+ into the cytosol (146). The activity of a Ca2+ dependent enzyme, phospholipase C (PLC), is increased by amphetamine, and PLC may be responsible for the increase in PKC beta(II) activity associated with amphetamine (146). Intracellular dopamine is also required for amphetamine- induced increases in PKC activity (146). Amphetamine increases the activity of phospholipase A2 (PLA2), perhaps by increasing intracellular pH (146). Low PLA2 activity may increase the activation of PKC, while high PLA2 activity may decrease the activation of PKC by amphetamine (146).
Amphetamine, a weak base, increases cytosolic dopamine and norepinephrine through two mechanisms. First, amphetamine inhibits vesicular sequestration of dopamine and norepinephrine into vesicles by directly interacting with vesicular monoamine transporter-2 (VMAT-2) (147). Second, amphetamine decreases VMAT-2 activity by reducing the pH gradients that drive monoamine uptake into vesicles (148).
At higher concentrations, amphetamine may act as a competitive antagonist at NMDA receptors (149). In addition, the drug is an agonist at TA1, a trace amine receptor (150).
Chemical Class:
dextro isomer of d,l-amphetamine sulfate
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
diazepam
Trade Name:
Valium ® [Roche]
IUPAC Name:
9-chloro-2-methyl-6-phenyl-
2,5-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-
5,8,10,12-tetraen-3-one
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Injectable/injection;
Concentrate/oral;
Gel/rectal
Major Metabolites:
nordiazepam;
temazepam;
oxazepam
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
11/15/1963
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Valium Tablet]
[Injectable]
[Gel]
[Concentrate]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C16H13ClN2O
Molecular Mass:
284.74 g/mol
Anxiety disorders or short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety; symptomatic relief of acute alcohol withdrawal; adjunct for the relief of skeletal muscle spasm due to reflex spasm to local pathology, spasticity caused by upper motor neuron disorders, athetosis, and stiff-man syndrome; adjunct for convulsive disorders
Diazepam is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (12). Diazepam is also an agonist at peripheral benzodiazepine receptors (48).
Chemical Class:
2-keto benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
divalproex sodium
Trade Name:
Depakote ® [Abbott Labs]
IUPAC Name:
sodium; 2-propylpentanoate;
2-propylpentanoic acid
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet (delayed release)/oral;
Capsule (delayed release pellets)/oral;
Tablet (extended release)/oral
Major Metabolites:
3-keto-valproic acid;
trans-2-ene valproic acid; valproic acid glucuronide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
03/10/1983
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Depakote Capsule]
[Depakote Tablet]
[Depakote ER Tablet]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C16H31NaO4
Molecular Mass:
310.405 g/mol
Indications:
Depakote ER Only: Manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder; prophylaxis of migraine headaches
All dosage forms: Monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of patients with complex partial seizures that occur either in isolation or in association with other types of seizures; sole or adjunctive therapy in the treatment of simple and complex absence seizures; adjunct for the treatment of patients with multiple seizure types that include absence seizures
Divalproex is a histone deacetylase inhibitor (49). The enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) activity by divalproex is possibly due to the downregulation of GAT-1 and GAT-3 GABA transporter proteins by the drug (50); the cause of this effect is currently unknown. Divalproex also inhibits succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (153). At voltage-gated sodium channnels, divalproex shifts the voltage dependence of steady-state inactivation to more hyperpolarized potentials (51); the degree to which this action occurs at therapeutically relevant concentrations in humans is currently not known (52). Finally, divalproex may inhibit T-type calcium channels (53).
Chemical Class:
carboxylic acid derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
doxepin hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Sinequan ® [Pfizer]
Common Chemical Name:
1-Propanamine,
3-
dibenz[b,e]oxepin-
11(6H)ylidene-N,N-dimethyl-,
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral;
Concentrate/oral;
Cream/topical
Major Metabolite:
desmethyldoxepin
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
09/23/1969
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Sinequan Capsule and Concentrate]
[Zonalon Cream]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C19H22ClNO
Molecular Mass:
315.837 g/mol
Indications:
Psychoneurotic patients with depression and/or anxiety; depression and/or anxiety associated with alcoholism (not to be taken concomitantly with alcohol); depression and/or anxiety associated with organic disease; psychotic depressive disorders with associated anxiety including involutional depression and bipolar disorders
Doxepin weakly inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine (54, 130) and serotonin (55, 130). It is a potent antagonist at histamine H1 (56, 57) and H2 receptors (57). Doxepin is also an antagonist at alpha-1-adrenoceptors (56). The drug binds to both serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors (7). In addition, it is an antagonist at all subtypes of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (58).
Chemical Class:
dibenzoxepin derivative (tertiary tricyclic)
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
duloxetine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Cymbalta ® [Eli Lilly]
IUPAC Name:
N-methyl-3-naphthalen-1-
yloxy-3-thiophen-2-yl-propan-
1-amine
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule, delayed release pellets/oral
Major Metabolites:
4-hydroxy duloxetine glucuronide;
6-hydroxy-5-methoxy duloxetine glucoronide;
4, 6-dihydroxy duloxetine glucoronide;
5-hydroxy, 6-methoxy duloxetine sulfate
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
08/03/2004
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C18H20ClNOS
Molecular Mass:
333.876 g/mol
Major depressive disorder; diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain
Duloxetine inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine (59).
Chemical Class:
thiophenepropanamine
PubChem 2D Structure:
Generic Name:
escitalopram oxalate
Trade Name:
Lexapro ® [Forest Labs]
IUPAC Name:
1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-1-
(4-
fluorophenyl)-1,3-
dihydroisobenzofuran-5-
carbonitrile; ethanedioic acid
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Capsule/oral;
Solution/oral
Major Metabolites:
S-demethylcitalopram;
S-didemethylcitalopram
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
08/14/2002
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C22H23FN2O5
Molecular Mass:
414.427 g/mol
Major depressive disorder
Escitalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) (45, 60).
Chemical Class:
S-enantiomer of the racemic bicyclic phthalane derivative citalopram
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
estazolam
Trade Name:
Prosom ® [Abbott Labs]
Common Chemical Name:
8-chloro-6-phenyl-4H-s-
triazolo[4,3-a]
[1,4]benzodiazepine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
1-oxo-estazolam;
4-hydroxy-estazolam
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/26/1990
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C16H11ClN4
Molecular Mass:
294.738 g/mol
Short-term treatment of insomnia
Estazolam is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (61).
Chemical Class:
triazolobenzodiazepine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
eszopiclone
Trade Name:
Lunesta ® [Sepracor]
IUPAC Name:
(7-oxo-2,5,8-triazabicyclo
[4.3.0]nona-1,3,5-
trien-9-yl) 2-(5-chloropyridin-
2-yl)-4-methyl-piperazine-1-
carboxylate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
(S)-zopiclone-N-oxide;
(S)-N-desmethyl zopiclone
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/15/2004
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H17ClN6O3
Molecular Mass:
388.808 g/mol
Treatment of insomnia
Eszopiclone is the S-isomer and biologically active component of zopiclone. Zopiclone potentiates GABA-induced chloride currents in GABA-A receptors that contain the alpha-1 subunit or the combination of the beta2 subunit and the gamma2 subunit (62).
pyrrolopyrazine derivative of the cyclopyrrolone class (S-isomer of zopiclone)
PubChem 2D Structure:

Generic Name:
fluoxetine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Prozac ® [Eli Lilly]
IUPAC Name:
N-methyl-3-phenyl-3-[4-
(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-
propan-1-amine hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Capsule/oral;
Solution/oral;
Capsule, delayed release pellets/oral (weekly)
Major Metabolite:
norfluoxetine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/29/1987
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Prozac Capsule, Prozac Solution, and Prozac Weekly Capsule]
[Fluoxetine Tablet]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H19ClF3NO
Molecular Mass:
345.787 g/mol
Major depressive disorder in adults, children, and adolescents; OCD in adults, children, and adolescents; bulimia nervosa; panic disorder
Fluoxetine inhibits the reuptake of serotonin (45). It is also an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2C receptors (7, 63).
Chemical Class:
bicyclic derivative of phenylpropylamine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
fluphenazine dihydrochloride
IUPAC Name:
2-[4-[3-[2-
(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazin-
10-yl]propyl]piperazin-1-
yl]ethanol
dihydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Injectable/injection;
Concentrate/oral;
Elixir/oral
Major Metabolites:
7-hydroxyfluphenazine;
fluphenazine sulfoxide;
fluphenazine N4-oxide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
08/24/1960
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[Injectable] [Concentrate]
[Elixir]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C22H28Cl2F3N3OS
Molecular Mass:
510.444 g/mol
Management of the manifestations of psychotic disorders
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Fluphenazine is an inverse agonist at dopamine D1 (64), D2 (27), D3 receptors (65), and D5 receptors (64, 66). Fluphenazine also binds with high affinity to dopamine D4 receptors (9). The drug is an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (24, 27). It has high affinities for serotonin 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 receptors (27, 29). In addition, fluphenazine is an antagonist at histamine H1 receptors (27). The drug also has high affinities for alpha-1A (27), alpha-1B (67), and alpha-2C-adrenoceptors (27).
Chemical Class:
piperazine phenothiazine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
flurazepam dihydrochloride
Trade Name:
Dalmane ® [Valeant]
IUPAC Name:
9-chloro-2-(2-diethylaminoethyl)-
6-(2-fluorophenyl)-2,5-
diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-
5,8,10,12-tetraen-3-one
dihydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolites:
N-1-desalkylflurazepam;
N-1-hydroxyethylflurazepam
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
04/07/1970
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C21H25Cl3FN3O
Molecular Mass:
460.799 g/mol
Short-term treatment of insomnia
Flurazepam is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (68).
Chemical Class:
2-keto benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
fluvoxamine maleate
Trade Name:
Luvox ® [Solvay]
IUPAC Name:
but-2-enedioic acid; 2-[5-
methoxy-1-[4-
(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-
pentylidene]aminooxyethanamine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Extended release capsule/oral
Major Metabolite:
fluvoxamine acid
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/05/1994
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C19H25F3N2O6
Molecular Mass:
434.407 g/mol
OCD in adults, children, and adolescents
Fluvoxamine is a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (69). It also acts as an agonist at sigma-1 receptors (70, 71).
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
haloperidol lactate
(also available as haloperidol or haloperidol decanoate)
IUPAC Name:
[4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-[4-(4-
fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-butyl]-4-
piperidyl]
2-hydroxypropanoate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Injectable/injection;
Solution/oral;
Concentrate/oral
Major Metabolites:
hydroxyhaloperidol (aka reduced haloperidol);
haloperidol pyridinium;
reduced haloperidol pyridinium;
haloperidol tetrahydropyridine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
04/12/1967
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[Injectable]
[Solution]
[Concentrate]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C21H23ClFNO2
Molecular Mass:
375.864 g/mol
Schizophrenia; control of tics and vocal utterances of Tourette's disorder
Haloperidol is an inverse agonist at dopamine D1 (64), D2 (72), D3 (65, 73), and D5 receptors (64). The drug is an antagonist at dopamine D4 receptors (74). It binds with relatively low affinity to serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (27). Haloperidol is a partial agonist at alpha-1-adrenoceptors (75). It is also an antagonist at sigma-1 receptors and an agonist at sigma-2 receptors (76).
Chemical Class:
butyrophenone
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
hydroxyzine dihydrochloride
IUPAC Name:
2-[2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)-
phenyl-methyl]piperazin-1-
yl]ethoxy]ethanol dihydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Capsule/oral;
Syrup/oral;
Injectable/injection;
Suspension/oral
Major Metabolite:
cetirizine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
04/12/1956
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C21H29Cl3N2O2
Molecular Mass:
447.825 g/mol
Indications:
For symptomatic relief of anxiety and tension associated with psychoneurosis and as an adjunct in organic disease states in which anxiety is manifested; management of pruritus due to allergic conditions such as chronic urticaria and atopic and contact dermatoses, and in histamine-mediated pruritus; as a sedative when used as pre-medication and following general anesthesia, hydroxyzine may potentiate meperidine and barbiturates, so their use in pre-anesthetic adjunctive therapy should be modified on an individual basis
Hydroxyzine is a histamine H1 receptor antagonist (77). The drug also binds to sigma-1 receptors (78, 79). It may bind to serotonin 5-HT2A receptors as well (80).
Chemical Class:
piperazine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
hydroxyzine pamoate
Trade Name:
Vistaril ® [Pfizer]
IUPAC Name:
4-[(3-carboxy-2-hydroxy-
naphthalen-1-yl)methyl]-3-
hydroxy-naphthalene-
2-carboxylic
acid; 2-[2-[4-[(4-
chlorophenyl)-phenyl-
methyl]piperazin-1-
yl]ethoxy]ethanol
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolite:
cetirizine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
11/15/1968
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C44H43ClN2O8
Molecular Mass:
763.274 g/mol
For symptomatic relief of anxiety and tension associated with psychoneurosis and as an adjunct in organic disease states in which anxiety is manifested; management of pruritus due to allergic conditions such as chronic urticaria and atopic and contact dermatoses, and in histamine-mediated pruritus; as a sedative when used as pre-medication and following general anesthesia, hydroxyzine may potentiate meperidine and barbiturates, so their use in pre-anesthetic adjunctive therapy should be modified on an individual basis
Hydroxyzine is a histamine H1 receptor antagonist (77). The drug also binds to sigma-1 receptors (78, 79). It may bind to serotonin 5-HT2A receptors as well (80).
Chemical Class:
piperazine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
imipramine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Tofranil ® [Tyco Healthcare]
Common Chemical Name:
5-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-
10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz
[b,f]azepine
monohydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
desipramine (aka desmethylimipramine);
2-hydroximipramine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
10/02/1959
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C19H25ClN2
Molecular Mass:
316.868 g/mol
Major depressive disorder, especially endogenous depression; childhood enuresis
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Imipramine inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine (81). It is an antagonist at histamine H1 and alpha-1-adrenoceptors (82, 130). In addition, the drug is an antagonist at M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (83).
Chemical Class:
tertiary dibenzazepine tricyclic
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
imipramine pamoate
Trade Name:
Tofranil-PM ® [Tyco Healthcare]
Common Chemical Name:
5-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-
10,11-dihydro-5H-
dibenz[b,f]azepine 4, 4'-
methylenebis-(3-hydroxy-
2-naphthoate) (2:1)
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolite:
desipramine (aka desmethylimipramine);
2-hydroximipramine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
03/11/1973
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C61H64N4O6
Molecular Mass:
949.184 g/mol
Major depressive disorder, especially endogenous depression
Imipramine inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine (81). Imipramine binds to both histamine H1 and alpha-1-adrenoceptors (82). In addition, the drug is an antagonist at M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (83).
Chemical Class:
tertiary dibenzazepine tricyclic
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
isocarboxazid
Trade Name:
Marplan ® [Oxford]
IUPAC Name:
N-benzylamino-5-methyl-
oxazole-3-carboxamide
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
benzylhydrazine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
07/01/1959
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C12H13N3O2
Molecular Mass:
231.251 g/mol
Major depressive disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Isocarboxazid is an irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) (84).
Chemical Class:
hydrazine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
lamotrigine
Trade Name:
Lamictal ® [GlaxoSmithKline]
IUPAC Name:
6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-
triazine-3,5-diamine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Chewable Tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
lamotrigine 2-N-glucuronide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/27/1994
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C9H7Cl2N5
Molecular Mass:
256.091 g/mol
The maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder to delay the time to occurrence of mood episodes (depression, mania, hypomania, mixed episodes) in patients treated for acute mood episodes with standard therapy; adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in adults and pediatric patients (>/= 2 years of age); adjunctive therapy for the generalized seizures of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in adult and pediatric patients (>/= 2 years of age)
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Lamotrigine blocks voltage-gated sodium channels in a use-dependent manner (85). The drug preferentially binds to the channel pore in inactivated but not resting sodium channels; its inhibition of sodium channels is therefore increased by neuronal depolarization (86). Lamotrigine also inhibits N-type and P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channels (87, 88).
Chemical Class:
phenyltriazine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
Trade Name:
Vyvanse ® [Shire]
IUPAC Name:
(2S)-2,6-diamino-N-[(2S)-1-phenylpropan-
2-yl]hexanamide; methanesulfonic acid
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolites:
p-hydroxyamphetamine;
p-hydroxynorephedrine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
02/23/2007
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H33N3O7S2
Molecular Mass:
455.58982 g/mol
ADHD
Vyvanse is a prodrug of dextroamphetamine. After oral administration, lisdexamfetamine dimesylate is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and converted to dextroamphetamine, which is responsible for the drug's activity.
Chemical Class:
prodrug of the dextro isomer of d,l-amphetamine sulfate
PubChem 2D Structure:
Generic Name:
lithium carbonate
Trade Name:
Eskalith ® [GlaxoSmithKline]
IUPAC Name:
dilithium carbonate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Capsule/oral;
Extended release tablet/oral
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
04/06/1970
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet/Capsule]
[Extended Release Capsule]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
CLi2O3
Molecular Mass:
73.8909 g/mol
Manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder or maintenance treatment for individuals with bipolar disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Please consult PubMed; the mechanisms of action of lithium are too complex to properly explain here.

Generic Name:
lithium citrate
IUPAC Name:
trilithium 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-
tricarboxylate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Syrup/oral
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
04/06/1970
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link] (syrup)
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C6H5Li3O7
Molecular Mass:
209.9227 g/mol
Manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder or maintenance treatment for individuals with bipolar disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Please consult PubMed; the mechanisms of action of lithium are too complex to properly explain here.

Generic Name:
lorazepam
Trade Name:
Ativan ® [Biovail]
IUPAC Name:
9-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-4-
hydroxy-2,5-
diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-
5,8,10,12-tetraen-3-one
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Injectable/injection;
Solution/oral;
Concentrate/oral
Major Metabolite:
lorazepam glucuronide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
09/30/1977
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[Injectable]
[Lorazepam Intensol Concentrate]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C15H10Cl2N2O2
Molecular Mass:
321.158 g/mol
Anxiety disorders or short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety or anxiety associated with depressive symptoms
Possible Mechanism of Action:
Lorazepam is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (12).
Chemical Class:
3-hydroxy benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
loxapine succinate
Trade Name:
Loxitane ® [Watson]
Common Chemical Name:
2-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-
piperazinyl)dibenz[b,f][1,4]
oxazepine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolites:
8-hydroxyloxapine;
7-hydroxyloxapine;
8-hydroxyamoxapine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
02/25/1975
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C22H24ClN3O5
Molecular Mass:
445.896 g/mol
Schizophrenia
Loxapine is an antagonist at dopamine D1 (89), D2 (90), and D3 receptors (91). The drug also binds to D4 and D5 receptors (67). It is an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (92) and an inverse agonist at 5-HT2C receptors (38). In addition, the drug has been found to bind to serotonin 5-HT6 receptors (27). It also binds with low affinity to 5-HT7 receptors (27). Additional binding sites of loxapine include alpha-1A-adrenoceptors, alpha-1B-adrenoceptors, and histamine H1 receptors (67).
Chemical Class:
tricyclic dibenzoxazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
maprotiline hydrochloride
Major Metabolites:
desmethylmaprotiline;
maprotiline N-oxide
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/01/1980
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C20H24ClN
Molecular Mass:
313.864 g/mol
Major Depressive Disorder
Maprotiline is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (93). It is also a potent histamine H1 receptor antagonist (94). The drug may act as an antagonist at some muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes (95, 96). Maprotiline is also a weak to moderate affinity antagonist of alpha-1-adrenoceptors (130).
Chemical Class:
tetracyclic
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
meprobamate
IUPAC Name:
[2-(carbamoyloxymethyl)-2-
methyl-pentyl] aminoformate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
2-hydroxymeprobamate;
meprobamate glucuronide;
meprobamate glucosyluronide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
04/28/1955
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C9H18N2O4
Molecular Mass:
218.25 g/mol
Anxiety disorders or short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety
Meprobamate is a barbiturate-like positive modulator of GABA-A receptor complexes (97).
Chemical Class:
propanediol dicarbamate
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
methamphetamine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Desoxyn ® [Ovation]
IUPAC Name:
N-methyl-1-phenyl-propan-2-
amine hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
amphetamine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/31/1943
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C10H16ClN
Molecular Mass:
185.693 g/mol
ADHD
Please consult PubMed; the mechanisms of action of methamphetamine are too complex to properly explain here.
amphetamine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
methylphenidate transdermal system
Trade Name:
Daytrana ® [Shire]
IUPAC Name:
methyl 2-phenyl-2-(2-
piperidyl)acetate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Extended release film; transdermal
Major Metabolite:
dl-ritalinic acid
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
4/06/2006
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C14H19NO2
Molecular Mass:
233.306 g/mol
ADHD
Methylphenidate inhibits the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine (3). The drug has a higher affinity (~ 10-fold) for dopamine transporters than norepinephrine transporters (3).
piperidine derivative in a multipolymeric adhesive
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
methylphenidate hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Ritalin ® [Novartis];
Concerta ® [Alza]
IUPAC Name:
methyl 2-phenyl-2-(2-
piperidyl)acetate hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Chewable tablet/oral;
Extended release tablet/oral;
Extended release capsule/oral;
Solution/oral
Major Metabolite:
dl-ritalinic acid
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/05/1955
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet - Ritalin]
[Extended Release Capsule - Ritalin LA]
[Extended Release Tablet - Concerta]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
[Link 2] (Concerta)
Empirical Formula:
C14H20ClNO2
Molecular Mass:
269.767 g/mol
ADHD, narcolepsy
Methylphenidate inhibits the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine (3). The drug has a higher affinity (~ 10-fold) for dopamine transporters than norepinephrine transporters (3).
piperidine derivative (a 50:50 mixture of racemic threo-methylphenidate hydrochloride)
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
mirtazapine
Trade Name:
Remeron ® [Organon]
Common Chemical Name:
1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-
methylpyrazino [2,1-a] pyrido
[2,3-c] benzazepine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Tablet/orally disintegrating
Major Metabolite:
desmethylmirtazapine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
06/14/1996
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[Orally Disintegrating Tablet]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H19N3
Molecular Mass:
265.353 g/mol
Major depressive disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Mirtazapine is an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT3 receptors (98). Mirtazapine is also an antagonist at alpha-2-adrenoceptors and histamine H1 receptors (98).
Chemical Class:
tetracyclic piperazinoazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
mixed amphetamine salts
Trade Name:
Adderall ® [Shire]
Drug Constituents:
dextroamphetamine saccharate; d,l-amphetamine aspartate monohydrate; dextroamphetamine sulfate; d,l-amphetamine sulfate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Extended release capsule/oral
Major Metabolite:
p-hydroxyamphetamine;
p-hydroxynorephedrine; norephedrine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
01/19/1960
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[Extended Release Capsule]
RxList:
[Link 1]
[Link 2] (XR)
Epocrates:
[Link]
ADHD
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
At plasmalemmal catecholamine transporters, amphetamine indirectly increases the efflux of cytosolic catecholamines so that they are released into the synaptic cleft (144). The drug causes the release of norepinephrine more potently than it causes the release of dopamine; it is much less effective as a serotonin releasing agent (144) The drug also directly inhibits norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake at higher concentrations (144). Amphetamine- induced activation of protein kinase C (PKC) beta(II) is responsible for the drug's effect on dopamine efflux (145). Na+ is cotransported with amphetamine as it enters neurons via catecholamine transporters; amphetamine-induced increases in intracellular Na+ may stimulate Na+/Ca2+ antiporters, resulting in an influx of Ca2+ into the cytosol (146). The activity of a Ca2+ dependent enzyme, phospholipase C (PLC), is increased by amphetamine, and PLC may be responsible for the increase in PKC beta(II) activity associated with amphetamine (146). Intracellular dopamine is also required for amphetamine- induced increases in PKC activity (146). Amphetamine increases the activity of phospholipase A2 (PLA2), perhaps by increasing intracellular pH (146). Low PLA2 activity may increase the activation of PKC, while high PLA2 activity may decrease the activation of PKC by amphetamine (146).
Amphetamine, a weak base, increases cytosolic dopamine and norepinephrine through two mechanisms. First, amphetamine inhibits vesicular sequestration of dopamine and norepinephrine into vesicles by directly interacting with vesicular monoamine transporter-2 (VMAT-2) (147). Second, amphetamine decreases VMAT-2 activity by reducing the pH gradients that drive monoamine uptake into vesicles (148).
At higher concentrations, amphetamine may act as a competitive antagonist at NMDA receptors (149). In addition, the drug is an agonist at TA1, a trace amine receptor (150).
amphetamine
Generic Name:
molindone hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Moban ® [Endo]
IUPAC Name:
3-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-oxa-4-
azoniacyclohex-4-ylmethyl)-
1,5,6,7-tetrahydroindol-4-one
chloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
Not known
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
01/18/1974
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C16H25ClN2O2
Molecular Mass:
312.835 g/mol
Schizophrenia
Molindone is an antagonist at dopamine D2 and D3 receptors (10). An unidentified metabolite of molindone may irreversibly inhibit monoamine oxidase A (151, 152).
Chemical Class:
dihydroindolone
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
nefazodone hydrochloride
IUPAC Name:
2-[3-[4-(3-
chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-
yl]propyl]-5-ethyl-4-(2-
phenoxyethyl)-1,2,4-triazol-3-
one
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
hydroxynefazodone;
triazoledione;
m-chlorophenylpiperazine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/22/1994
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C25H33Cl2N5O2
Molecular Mass:
506.467 g/mol
Major depressive disorder
Nefazodone is an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (99). It weakly inhibits serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake (99). Nefazodone is an antagonist at histamine H1 receptors and alpha-1-adrenoceptors (45). The drug also binds to 5-HT1A receptors (45, 82) and alpha-2-adrenoceptors (45).
Chemical Class:
phenylpiperazine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
nortriptyline hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Pamelor ® [Tyco Healthcare]
Common Chemical Name:
1-Propanamine, 3-(10,11-
dihydro,
5H-dibenzo [a, d]
cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-N-
methyl-,hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral;
Solution/oral
Major Metabolite:
10-hydroxynortriptyline
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
11/06/1964
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C19H22ClN
Molecular Mass:
299.837 g/mol
Major depressive disorder, especially endogenous depression
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Nortriptyline inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine (100). At serotonin 5-HT2A receptors, nortriptyline is an antagonist (101). The drug is also a low potency antagonist at histamine H1 receptors (102) and some subtypes of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (103).
dibenzocycloheptadiene (tricyclic)
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
olanzapine
Trade Name:
Zyprexa ® [Eli Lilly]
Common Chemical Name:
2-methyl-4-(4-methyl-1-
piperazinyl)-10H-thieno[2,3-b]
[1,5]benzodiazepine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Injectable/intramuscular;
Tablet/orally disintegrating
Major Metabolites:
olanzapine 10-N-glucuronide;
olanzapine 4'-N-glucuronide;
4'-N-desmethylolanzapine;
olanzapine N-oxide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
09/30/1996
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H20N4S
Molecular Mass:
312.434 g/mol
Schizophrenia; acute monotherapy of acute mixed or manic episodes associated with bipolar I disorder; maintenance monotherapy of bipolar patients; combination with lithium or valproate for the short-term treatment of manic episodes associated with bipolar I disorder; Zyprexa intramuscular is indicated for the treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia and bipolar I mania
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Olanzapine is a low potency antagonist at dopamine D1 receptors (104, 105). In addition, olanzapine acts as an inverse agonist at dopamine D2 receptors (106). The drug is an antagonist at dopamine D3 (107) and D4 receptors (74). At serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors, olanzapine is a potent antagonist (105). It also exhibits potent antagonist effects at histamine H1 receptors and alpha-1 adrenoceptors (105). Olanzapine is a low affinity antagonist at M1 and M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (105).
Chemical Class:
thienobenzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
olanzapine and fluoxetine
hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Symbyax ® [Eli Lilly]
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
Initial Approval:
12/24/2003
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Molecular Mass:
658.23 g/mol
Depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder
Please refer to the entries for olanzapine and fluoxetine hydrochloride.
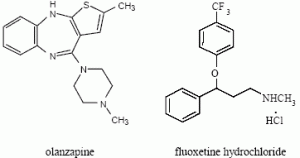
Generic Name:
oxazepam
IUPAC Name:
9-chloro-4-hydroxy-6-phenyl-
2,5-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-
5,8,10,12-tetraen-3-one
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolite:
oxazepam
glucuronide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
06/04/1965
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C15H11ClN2O2
Molecular Mass:
286.713 g/mol
Anxiety disorders or short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety; anxiety associated with depression; management of anxiety, tension, agitation, and irritability in older patients; acute tremulousness, inebriation, or anxiety associated with alcohol withdrawal
Oxazepam is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (108).
3-hydroxy benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
paliperidone
Trade Name:
Invega ® [Janssen]
IUPAC Name:
3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzoxazol-3-
yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl]-9-hydroxy-2-
methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydropyrido[2,1-
b]pyrimidin-4-one
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Extended release tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
Paliperidone is not metabolized extensively, and none of its metabolites could be considered "major."
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/19/2006
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C23H27FN4O3
Molecular Mass:
426.483883 g/mol
Acute and maintenance treatment of schizophrenia
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Paliperidone is a centrally active dopamine Type 2 (D2) antagonist and with predominant serotonin Type 2 (5HT2A) activity (see prescribing information). Paliperidone is also active as an antagonist at α1 and α2 adrenergic receptors and H1 histaminergic receptors (see prescribing information).
Chemical Class:
benzisoxazole derivative (major active metabolite of risperidone)
PubChem 2D Structure:
Generic Name:
paroxetine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Paxil ® [GlaxoSmithKline]
Common Chemical Name:
(-)-trans-4R-(4'-
fluorophenyl)-3S-[(3',4'-
methylenedioxyphenoxy)
methyl]
piperidine
hydrochloride
hemihydrate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Extended release tablet/oral;
Suspension/oral
Major Metabolites:
(3S,4R)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-
hydroxymethyl-1-
methylpiperidine;
3S,4R)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-
(hydroxymethyl)piperidine;
(3S,4R)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-
(4-
hydroxy-3-
methoxyphenoxymethyl)
piperidine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/29/1992
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet & Suspension]
[Extended Release Tablet - Paxil CR]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C19H20FNO3 ·HCl·1/2H2O
Molecular Mass:
374.8 g/mol
Major depressive disorder; OCD; panic disorder; social anxiety disorder/social phobia; generalized anxiety disorder (GAD); PTSD
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Paroxetine is a potent serotonin reuptake inhibitor (45). It also has a moderate affinity for the norepinephrine transporter (45). Paroxetine is a low affinity antagonist at some subtypes of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (45). In addition, paroxetine is a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (143).
phenylpiperidine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
paroxetine mesylate
Trade Name:
Pexeva ® [Synthon]
IUPAC Name:
methanesulfonic acid; 3-
(benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-
yloxymethyl)-4-phenyl-piperidine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
(3S,4R)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-
hydroxymethyl-1-
methylpiperidine;
3S,4R)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-
(hydroxymethyl)piperidine;
(3S,4R)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-
(4- hydroxy-3-
methoxyphenoxymethyl)
piperidine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
07/03/2003
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C20H25NO6S
Molecular Mass:
407.482 g/mol
Major depressive disorder; OCD; panic disorder; social anxiety disorder/social phobia; generalized anxiety disorder (GAD); PTSD
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Paroxetine is a potent serotonin reuptake inhibitor (45). It also has a moderate affinity for the norepinephrine transporter (45). Paroxetine is a low affinity antagonist at some subtypes of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (45). In addition, paroxetine is a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (143).
phenylpiperidine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
perphenazine
IUPAC Name:
2-[4-[3-(2-chlorophenothiazin-
10-yl)propyl]piperazin-1-
yl]ethanol
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Concentrate/oral
Major Metabolites:
deshydroxyethylperphenazine;
perphenazine sulfoxide;
7-hydroxyperphenazine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
02/27/1957
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C21H26ClN3OS
Molecular Mass:
403.969 g/mol
Schizophrenia; control of severe nausea and vomiting in adults
Perphenazine is a potent dopamine D2 receptor antagonist (110). It is also an antagonist at dopamine D1 (110), D3 (10), and D4 (10) receptors. At histamine H1 receptors, perphenazine is an antagonist (27). The drug also binds to serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors (27). In addition, perphenazine binds to alpha-1-adrenoceptors (27) and sigma receptors (111).
Chemical Class:
piperazinyl phenothiazine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
phenelzine sulfate
Trade Name:
Nardil ® [Pfizer]
IUPAC Name:
2-hydrazinylethylbenzene;
sulfuric acid
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
phenylacetic acid;
parahydroxyphenylacetic acid
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
06/09/1961
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C8H14N2O4S
Molecular Mass:
234.274 g/mol
Indications:
Depressed patients clinically characterized as "atypical," "nonendogenous," or "neurotic." These patients often have mixed anxiety and depression and phobic or hypochondriacal features. There is less conclusive evidence of its usefulness with severely depressed patients with endogenous features.
Nardil should rarely be the first antidepressant drug used. Rather, it is more suitable for use with patients who have failed to respond to the drugs more commonly used for these conditions.
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Phenelzine is an irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) (111). The drug also inhibits GABA transaminase and alanine transaminase (111).
hydrazine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
prochlorperazine dimaleate
Trade Name:
Compazine ® [GlaxoSmithKline]
IUPAC Name:
2-chloro-10-[3-(4-methyl-
2,3,5,6-tetrahydropyrazin-1-
yl)propyl]-10H-phenothiazine;
4-hydroxy-4-oxo-but-2-enoate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Suppository/rectal
Major Metabolite:
prochlorperazine sulphoxide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
10/23/1956
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C24H28ClN3O4S
Molecular Mass:
606.088 g/mol
Schizophrenia; control of severe nausea and vomiting; short-term treatment of generalized non-psychotic anxiety (should not be the first drug used in therapy)
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Prochlorperazine is an antagonist at dopamine D2 receptors (112). Prochlorperazine also binds to dopamine D3 (113) and D4 (10) receptors. In addition, the drug binds to serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (29), histamine H1 receptors (114), and alpha-1-adrenoceptors (114).
Chemical Class:
piperazine phenothiazine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
protriptyline hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Vivactil ® [Odyssey]
Common Chemical Name:
N-methyl-5H-dibenzo[a,d]-
cycloheptene-5-propanamine
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
protriptyline 10,11 expoxide;
10-hydroxyprotriptyline;
10,11-dihydroxyprotriptyline
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
09/27/1967
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C19H22ClN
Molecular Mass:
299.837 g/mol
Treatment of symptoms of depression in patients who are under close medical supervision. Its activating properties make it particularly suitable for withdrawn and anergic patients
Protriptyline is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (115). The drug is an antagonist at some subtypes of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (117, 130). It is also a low affinity antagonist at histamine H1 receptors (102, 130).
dibenzocycloheptene derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
quazepam
Trade Name:
Doral ® [MedPointe]
IUPAC Name:
9-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-
(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-2,5-
diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-
5,8,10,12-tetraene-3-thione
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
2-oxoquazepam;
N-desalkyl-2-oxoquazepam
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/27/1985
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H11ClF4N2S
Molecular Mass:
386.795 g/mol
Short-term treatment of insomnia
Possible Mechanism of Action:
Quazepam binds to GABA-A receptor complexes that contain the alpha1 subunit (118).
Chemical Class:
trifluoroethyl benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
quetiapine fumarate
Trade Name:
Seroquel ® [AstraZeneca]
Common Chemical Name:
2-[2-(4-dibenzo [b,f ]
[1,4]thiazepin-11-yl-1-
piperazinyl)ethoxy]-ethanol
fumarate (2:1) (salt)
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Extended release tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
quetiapine sulfoxide;
7-hydroxyquetiapine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
09/26/1997
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[Extended Release Tablet - Seroquel Xr]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C46H54N6O8S2
Molecular Mass:
883.089 g/mol
Schizophrenia; acute manic episodes associated with bipolar I disorder, as either monotherapy or adjunct therapy to lithium or divalproex
Quetiapine is an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (119). It is also a low potency dopamine D2 receptor inverse agonist (106). Quetiapine is an antagonist at alpha-1A-adrenoceptors (25), alpha-1B-adrenoceptors (25), and alpha-2C-adrenoceptors (40). In addition, the drug is a histamine H1 receptor antagonist (27).
dibenzothiazepine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
ramelteon
Trade Name:
Rozerem ® [Takeda]
Common Chemical Name:
(S)-N-[2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-
2H-indeno-[5,4-b]furan-8-
yl)ethyl]propionamide
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
M-II
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/29/1993
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C16H21NO2
Molecular Mass:
259.343 g/mol
Insomnia characterized by difficulty with sleep onset
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Ramelteon is an agonist at melatonin M1 and M2 receptors.

Generic Name:
risperidone
Trade Name:
Risperdal ® [Janssen]
IUPAC Name:
4-[2-[4-(6-fluorobenzo[d]
isoxazol-3-yl)-1-
piperidyl]ethyl]-3-methyl-2,6-
diazabicyclo[4.4.0]deca-1,3-
dien-5-one
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Tablet/orally disintegrating;
Solution/oral
Major Metabolite:
9-hydroxyrisperidone
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/29/1993
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablets & Solution]
[Intramuscular - Risperdal Consta]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C23H27FN4O2
Molecular Mass:
410.485 g/mol
Schizophrenia; short-term treatment of acute manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder; combination therapy with lithium or valproate for the short-term treatment of acute manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Risperidone is a high potency antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (120). The drug also acts as an inverse agonist at dopamine D2 receptors (106) and is an antagonist at D3 and D4 receptors (120). Risperidone is an inverse agonist at serotonin 5-HT1B (121), 5-HT1D (121), and 5-HT2C (38, 122) receptors. It acts as an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT7 (123) receptors. In addition, risperidone is an antagonist at alpha-1A-adrenoceptors (25), alpha-1B-adrenoceptors (25), alpha-2C-adrenoceptors (40), and histamine H1 receptors (27).
benzisoxazole derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
selegiline transdermal system
Trade Name:
EMSAM ® [Somerset]
IUPAC Name:
N-methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-
ynyl-propan-2-amine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Extended release film/transdermal
Major Metabolites:
N-desmethylselegiline;
L-methamphetamine;
L-amphetamine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
02/27/2006
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Prescribing Information:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C13H17N
Molecular Mass:
187.28078 g/mol
Indications:
Major depressive disorder
Selegiline is an irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) and monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) according to the prescribing information for the drug. Selegiline has a greater affinity for MAO-B and is therefore selective for MAO-B at lower dosages (see the prescribing information).
Chemical Class:
levorotatory acetylenic derivative of phenethylamine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
sertraline hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Zoloft ® [Pfizer]
IUPAC Name:
4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-
methyl-tetralin-1-amine
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Concentrate/oral
Major Metabolites:
desmethylsertraline
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/30/1991
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet & Concentrate]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H18Cl3N
Molecular Mass:
342.69 g/mol
Major depressive disorder; OCD in adults, children, and adolescents;, panic disorder; PTSD; premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD); social anxiety disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Sertraline inhibits the reuptake of serotonin (45). It is also a low potency dopamine reuptake inhibitor (16).

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
temazepam
Trade Name:
Restoril ® [Tyco Healthcare]
IUPAC Name:
9-chloro-4-hydroxy-2-methyl-
6-phenyl-2,5-
diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-
5,8,10,12-tetraen-3-one
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolite:
temazepam glucuronide
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
02/27/1981
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C16H13ClN2O2
Molecular Mass:
300.739 g/mol
Short-term treatment of insomnia
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Temazepam is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (61).
3-hydroxy benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
thioridazine hydrochloride
IUPAC Name:
10-[2-(1-methyl-2-
piperidyl)ethyl]-2-
methylsulfanyl-phenothiazine hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Concentrate/oral
Major Metabolites:
mesoridazine;
sulforidazine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
03/15/1962
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C21H27ClN2S2
Molecular Mass:
407.037 g/mol
Management of schizophrenic patients who fail to respond adequately with other antipsychotic drugs
Thioridazine binds to dopamine D2, D3, and D4 receptors (67). The drug is an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (24). Thioridazine is also an antagonist at alpha-1A-adrenoceptors and alpha-1B-adrenoceptors (25). In addition, it is an antagonist at M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (28). Finally, thioridazine is an antagonist at histamine H1 receptors (27).
Chemical Class:
piperidine phenothiazine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
thiothixene
Trade Name:
Navane ® [Pfizer]
IUPAC Name:
N,N-dimethyl-9-[3-(4-
methylpiperazin-1-
yl)propylidene]thioxanthene-2-
sulfonamide
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral;
Injectable/injection;
Concentrate/oral
Major Metabolites:
N/A (E-mail Shawn if you can provide this information.)
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
07/24/1967
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C23H29N3O2S2
Molecular Mass:
443.627 g/mol
Schizophrenia
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Thiothixene binds to dopamine D2 receptors, histamine H1 receptors, alpha-1A-adrenoceptors, and serotonin 5-HT7 receptors (27). It also has a moderate affinity for alpha-1B-adrenoceptors (67).
thioxanthene
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
tranylcypromine sulfate
Trade Name:
Parnate ® [GlaxoSmithKline]
IUPAC Name:
(2-phenylcyclopropyl)
ammonium
sulfate
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
N-acetyltranylcypromine;
p-hydroxytranylcypromine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
02/21/1961
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C18H24N2O4S
Molecular Mass:
364.46 g/mol
Major depressive episode without melancholia
Tranylcypromine is an irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) (125).
cyclopropylamine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
trazodone hydrochloride
IUPAC Name:
8-[3-[4-(3-
chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-
yl]propyl]-6,8,9-
triazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-2,4,9-
trien-7-one hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
m-chlorophenylpiperazine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/24/1981
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C19H23Cl2N5O
Molecular Mass:
408.324 g/mol
Major depressive disorder
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Trazodone and its active metabolite,
m-chlorophenylpiperazine (m-CPP), are partial agonists at serotonin 5-HT1A receptors (126). At serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors, trazodone is an antagonist (127). Trazodone and m-CPP are full agonists at serotonin 5-HT2C receptors (128). However, trazodone has a much lower affinity for 5-HT2C receptors than m-CPP (127). The drug is an antagonist at alpha-1-adrenoceptors (129, 130) and a very low affinity antagonist at histamine H1 receptors (130). In addition, m-CPP causes the extracellular release of serotonin through the serotonin transporter (131).
Chemical Class:
triazolopyridine derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
triazolam
Trade Name:
Halcion ® [Pfizer]
Common Chemical Name:
8-chloro-6-(o-chlorophenyl)-1-
methyl -4H-s-triazolo-(4,3-
alpha)(1,4)
benzodiazepine
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral
Major Metabolites:
alpha-hydroxytriazolam;
4-hydroxytriazolam
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
11/15/1982
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H12Cl2N4
Molecular Mass:
343.21 g/mol
Short-term treatment of insomnia
Possible Mechanism of Action:
Triazolam is a nonselective benzodiazepine agonist (132).
triazolo benzodiazepine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
trifluoperazine dihydrochloride
Trade Name:
Stelazine ® [GlaxoSmithKline]
IUPAC Name:
10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-
yl)propyl]-2-
(trifluoromethyl)phenothiazine
dihydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Concentrate/oral
Major Metabolites:
N-desmethyltrifluoperazine;
7-hydroxytrifluoperazine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
04/16/1959
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C21H26Cl2F3N3S
Molecular Mass:
480.418 g/mol
Schizophrenia; short-term treatment of generalized non-psychotic anxiety (should not be used as the first drug in therapy for most patients)
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Trifluoperazine is an inverse agonist at dopamine D2 receptors (133). The drug also binds with moderate affinity to dopamine D4 receptors (134). The drug is an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (135) as well as alpha-1A-adrenoceptors and alpha-1B-adrenoceptors (25). Trifluoperazine is a low affinity antagonist at histamine H1 receptors (136). In addition, the drug inhibits interactions between calmodulin and proteins (137).
Chemical Class:
piperazine phenothiazine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
trimipramine maleate
Trade Name:
Surmontil ® [Odyssey]
Common Chemical Name:
5-(3-dimethylamino-2-
methylpropyl)-10,11-dihydro-
5H-dibenz (b,f) azepine acid
maleate
(racemic form)
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolites:
desmethyltrimipramine
2-hydroxytrimipramine;
2-hydroxydesmethyltrimipramine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
06/12/1979
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C24H30N2O4
Molecular Mass:
410.506 g/mol
Major depressive disorder, especially endogenous depression
Trimipramine is an antagonist at alpha-1A-adrenoceptors and alpha-1B-adrenoceptors (130, 138) as well as histamine H1 receptors (130). The drug also displays high affinities for serotonin 5-HT2A receptors and dopamine D2 receptors (138).
dibenzazepine (tertiary tricyclic)
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
venlafaxine hydrochloride
Trade Name:
Effexor ® [Wyeth]
IUPAC Name:
1-[2-dimethylamino-1-(4-
methoxyphenyl)-
ethyl]cyclohexan-1-ol
hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Extended release capsule/oral
Major Metabolite:
O-desmethylvenlafaxine
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/28/1993
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[Extended Release Capsule - Effexor XR]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H28ClNO2
Molecular Mass:
313.862 g/mol
Major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder (XR version only), panic disorder (XR version only), social anxiety disorder (XR version only)
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Venlafaxine inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine (139, 140). It has a much greater affinity for the serotonin transporter (139).
Chemical Class:
phenethylamine bicyclic derivative
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
zaleplon
Trade Name:
Sonata ® [King/Wyeth]
IUPAC Name:
N-[3-(9-cyano-2,6,7-
triazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-
2,4,7,9-tetraen-5-yl)phenyl]-
N-ethyl-ethanamide
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolite:
5-oxo-zaleplon
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
08/13/1999
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C17H15N5O
Molecular Mass:
305.334 g/mol
Short-term treatment of insomnia
Possible Mechanism of Action:
Zaleplon binds to GABA-A receptor complexes that contain the alpha1 subunit(132).
Chemical Class:
pyrazolopyrimidine
PubChem 2D Structure:

"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
ziprasidone hydrochloride
monohydrate
Trade Name:
Geodon ® [Pfizer]
IUPAC Name:
6-chloro-5-[2-[4-(7-thia-8-
azabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-1,3,5,8-
tetraen-9-yl)piperazin-1-
yl]ethyl]-1,3-dihydroindol-2-
one
hydrate hydrochloride
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Capsule/oral
Major Metabolites:
benzisothiazole sulphoxide; benzisothiazole sulphone; ziprasidone sulphoxide;
S-methyl-dihydroziprasidone
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Manufacturer:
Pfizer
Initial Approval:
02/05/2001
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Link]
RxList:
[Link]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C21H24Cl2N4O2S
Molecular Mass:
467.412 g/mol
Schizophrenia; acute manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar disorder, with or without psychotic features
Possible Mechanisms of Action:
Ziprasidone is an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors and dopamine D2 receptors (141). The drug is a partial agonist at serotonin 5-HT1B receptors and an inverse agonist at 5-HT1D receptors (121). Ziprasidone is also an inverse agonist at 5-HT2C receptors (38). The drug is an agonist at 5-HT1A receptors (142) and is known to bind to 5-HT7 receptors (27). Ziprasidone may bind to dopamine D1, D3, and D4 receptors (67). Finally, ziprasidone is a low affinity antagonist at alpha-1-adrenoceptors and histamine H1 receptors (141).
Chemical Class:
benzisothiazolyl piperazine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]
Generic Name:
zolpidem tartrate
Trade Name:
Ambien ® [Sanofi-Aventis]
IUPAC Name:
2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid;
N,N-dimethyl-2-[4-methyl-8-
(4-methylphenyl)-6,9-
diazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-
2,4,7,9-tetraen-7-yl]-
ethanamide
Dosage Forms/Routes:
Tablet/oral;
Extended release tablet/oral
Major Metabolite:
"M-3"
Database Search Links:
[PubMed]
[Search PubMed for
Randomized
Controlled Trials]
[PubChem]
[PDSP Ki database]
Initial Approval:
12/16/1992
Manufacturers:
[FDA Search]
Product Insert:
[Tablet]
[Extended Release Tablet - Ambien CR]
Epocrates:
[Link]
Empirical Formula:
C42H48N6O8
Molecular Mass:
764.866 g/mol
Short-term treatment of insomnia
Possible Mechanism of Action:
Zolpidem binds to GABA-A receptor complexes that contain the alpha1 subunit (132).
Chemical Class:
imidazopyridine
PubChem 2D Structure:
"3D" Structure (Requires Chime):
[Link]



































